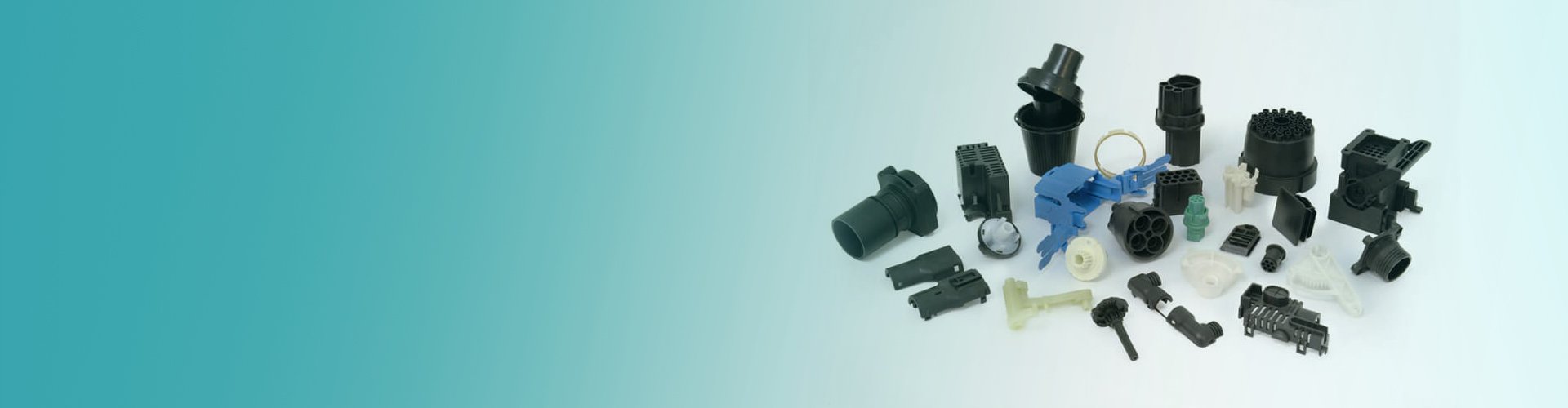
Insert Molding
Insert molding describes an injection molding procedure that entails molding plastic material about an insert to form finished product that integrate several materials. Most manufacturers use metal inserts for enhancing the mechanical characteristic of the thermoplastic part. The process can offer solutions for an expansive scope of design and manufacturing needs.
Advantages of Insert Molding
Injection molding procedure has been constantly improved to adapt to the ever-advancing requirements of current manufacturing..
Improved Mechanical Properties – The process ensures a strong fusion between the plastic material and insert, providing enhanced durability and structural integrity.
Lowered Manufacturing and Labor Costs – Merging several parts into one unit does away with the necessity for independent assembly operations, which saves on production and labor expenses.
Reduced Weight and Size – Insert injection molding gives smaller plastic parts that have lighter weight. This is because the process eliminates the requirement for fasteners and connectors.
Design Versatility – The process allows for integration of different materials, which offers a variety of design potential.
Streamlined Production and Cycle Time – Plastic insert molding process makes the manufacturing workflow very simple, facilitating faster cycle times and greater yield, desired application.


When to Consider Insert Molding
You should opt for insert injection molding of plastic parts when producing items that possess the following features:
- When dealing with a pre-formed substrate.
- When the substrate comprises of wires, metals, or computerized parts.
- The end product ought to be a rigid item.
- When you need to encase a metal or additional non-plastic part using a plastic resin or polymer, for example screwdriver.


The process of plastic insert molding entails fusing pre-fabricated components or inserts with melted plastic to develop a single consolidated part. You can use a myriad of materials for both the plastic part and the insert.
However, proper selection of material in necessary to attain optimal functionality and efficiency of the insert molded product. It is for this matter that we are going to highlight the popular materials employed in insert injection molding operation:
Material as Inserts
Metals:
Are commonly utilized because of their conductivity, strength, and longevity. Copper, brass, aluminum and stainless steel are some of the frequently used metal inserts. They are deployed in insert injection molding applications requiring high electrical conductivity and mechanical strength.
Plastics:
These are used particularly if compatibility with thermoplastic molding material is crucial. The plastic inserts can be made from polyethylene, polycarbonate, or nylon, which give better chemical compatibility, and lower galvanic corrosion risk.
Plastic Molding Material
Thermoplastics: These are the most preferred insert injection molding materials because of their capability to be melted and redesigned severally. The following are the common thermoplastics used:
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Preferred for its impact resistance, strength, and versatility.
Polycarbonate (PC): Gives good heat resistance, exceptional impact resistance, and high transparency.
Nylon (PA): Ensures superior chemical resistance, low friction, and high strength.
Polypropylene (PP): Popular for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightweight.
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT): Provides outstanding electrical properties, high heat resistance, and good dimensional stability.
Thermosetting Plastics: Though rarely used, certain insert plastic molding applications might necessitate the utilization of thermosetting plastics, like melamine resins, phenolic resins, and epoxy resins. These materials undergo permanent curing if subjected to heat or additional curing media. Thermosetting plastics offer outstanding electrical insulation capabilities, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.
It is essential to choose insert molding materials which are compatible with regard to performance, adhesion, and thermal expansion specifications.
Insert Molding Techniques


There are two common methods of placing the insert components inside the mold. The techniques ensure correct positioning and fusion of the insert with the molten plastic material.
Manual Insert Molding
This is where you place the insert manually into the mold chamber prior to injecting the molten plastic. It facilitates more control over the injection molding operation and is suitable for fabricating extremely complex parts or small-scale manufacturing runs.
Even so, manual insert injection molding process can require more workforce, which increases labor expenses and eventually production costs. Moreover, the manual components handling might result in inconsistency and variability in the end product.
Automatic Insert Molding
Contrary to the manual method, automated insert plastic molding employs automation systems and robotics to put the inserts in the molds. The method provides numerous benefits, including enhanced accuracy, speed and consistency throughout the fabrication operation.
Automation minimizes the chances of human error and decreases labor expenses, which makes it perfect option for bulk production runs. Automatic insert injection molding is often employed in the fabrication of electronic gadgets and other uses where consistency and bulk output are critical.
Insert Molding Process


Plastic insert molding is fairly similar to ordinary injection molding process. It entails melting and feeding molten thermoplastic into a mold employing similar injection molding equipment utilized in standard plastic molding operation.
However, integration of inserts is the major difference between the two procedures. Below are the 5 stages of plastic insert molding process:
Step 1: Insert Placement in the Mold
Place the insert correctly in the mold chamber in the preferred position. You can put the insert within the mold either manually or automatically. It might be clasped in place employing mechanisms like holes, grooves, or mechanical techniques.
The insert component can be fabricated independently, and be created using plastic, metal, or alternative materials. You can machine it to the preferred size and shape or use pre-formed insert.
Designing the mold for insert injection molding should factor in the insert position inside the mold. Proper placement of the insert ensures it maintains its location and orientation.
Step 2: Plastic Material Injection
An injection system aids in feeding the melted thermoplastic within the mold cavity. The procedure happens under elevated pressure, which pushes the plastic material to occupy all sections of the mold. The pressure also eliminates all the air via the mold vents and ensures that the plastic sticks perfectly to the insert component.
Step 3: Cooling and Curing
Following injection of the molten plastic, it is left in the mold to cool and cure. Cooling duration can differ based on the part complexity and material employed. It is essential to maintain the material at defined temperature to enable even curing. Additionally, sustaining a holding pressure assists in minimizing shrinking effects whilst making sure there is no backflow into the molten plastic tank.
Step 4: Finished Part Removal
After curing, you open the mold and remove the finished part having the insert permanently encapsulated or fused within it.
Step 5: Post Processing
The insert-molded component will often undergo extra processing before being ejected from the production line. Some of the popular secondary treatments performed include:
Deburring:
Involves taking out excess material that impacts the molded part appearance. Manual trimming using relevant tools is the common deburring method applied.
Heat Treatment:
Is instrumental in eliminating internal stress that could lower the quality of finished part. The heat treatment ought to be 10-20 degrees Celsius greater than the part’s operating temperature or below its deformation temperature.
Surface Finish:
You can apply various surface finishing techniques like electroplating and printing. The select methods is dictated by the design requirements. Some finishes enhance material physical properties, whilst others incorporate aesthetic impacts to the finished part.
Humidity Control
The objective of this treatment is to ensure molded product insulation from air, quicken absorption of moisture, avoid oxidation, and stabilize size. It entails immersing the molded part inside hot water having temperatures between 80-100 degrees Celsius.
Insert Injection Molding Limitations


Some of the disadvantages of insert injection molding include:
Higher Upfront Costs – The initial plastic insert molding cost can be greater because of the necessity for specialized equipment and molds. Nevertheless, these expenses might be counterbalanced by savings in assembly and manpower in the long-term.
Complex Mold Designs – Molds Designing and production can be challenging in comparison to molds used in conventional plastic injection molding, as they require more skills.
Material Compatibility – All materials are not compatible with the process. Therefore, you should choose compatible materials capable of withstanding the pressure and heat experienced during the process of injection molding.
Regardless of these limitations, the numerous advantages of insert injection molding qualifies it as an ideal alternative for making intricate, multi-material parts. It is particularly perfect for applications that need tough metal components and high-performance plastic parts.
Insert Molding Vs Over molding


Plastic insert molding and over molding allow manufacturers to form multi-material items without utilizing adhesives. This aids in eliminating secondary assembly processes, and enhance quality of the end product.
Nonetheless, there are noteworthy differences between over molding and insert plastic molding as highlighted below:
Process – Overmolding entails two shot injection of the materials to develop the over mold and the substrate. On the other hand, insert injection molding entails just a single shot of the melted plastic.
Speed – Due to the one-shot injection of raw material, cycle time of insert plastic molding process is faster in comparison to over molding operation. Nevertheless, this does not certainly imply that insert injection molding is normally the fastest alternative for manufacturing.
In certain instances, finding pre-fabricated inserts that match the specifications can be challenging. Therefore, there will be necessity to form a custom insert that can prolong the duration of production.
Cost – Plastic over molding and insert injection molding accelerate production and lower the assembly costs. This helps in cutting the costs of production whilst at the same time increasing profits when involving in mass production of parts.
But, over molding is costlier compared to insert molding operation since it entails two stages. This is especially true with regard to small production runs or prototype fabrication. The process needs two separate tools for the over mold and substrate.
Material – Over molded parts are fabricated using plastic materials capable of forming chemical bonds between them. But not all plastic polymers are chemically compatible. However, most plastics are adaptable with non-plastic materials. For this reason, insert injection molding allows for a wider material compatibility.
Insert Molding Design Considerations
There are some essential design parameters that you should consider to enjoy the full benefits of insert plastic molding process. Paying attention to the parameters will ensure reduced costs, enhanced design versatility, and lead to successful fabrication of intricate, multi-material parts for a variety of applications.
Material Selection and Part Geometry
It is important to factor in the material and geometry of both plastic component and insert during designing of insert molding product. The selected material will considerably influence the appearance, durability and performance of end product.
Choose materials that are compatible with one another and capable of enduring the pressure and high temperature of the process. Moreover, geometry of the molded component and insert need to guarantee proper integration and bonding.
Insert Positioning and Alignment
Proper placement and alignment of the insert are critical in realizing a successful molding operation. Poorly aligned components can result in improper bonding, leading to a defective or weakened finished product.
To attain accurate positioning, incorporate mechanisms in the mold cavity that firmly grip the insert in the right position throughout the process. The mechanism can consist of special pins, channels, or cavities inside the mold matching the insert shape.
Correct insert positioning improves the structural integrity of the end product and assist in streamlining the manufacturing process and reduce flaws.
Design and Fabrication of Molding Tool
The mold’s design and fabrication serve a critical purpose during the insert plastic molding operation. Using a well-modelled mold will ensure precise representation of the final product geometry, which leads to correct bonding of the insert and plastic materials.
The mold design ought to accommodate the various materials and steps production steps involved whilst retaining the finished product integrity. There are numerous variables to consider during the mold designing.
Factor in the plastic type being utilized, insert and plastic component dimensions, and needed production volume. Modern mold designs might consist of features like ejection mechanism or cooling channels to minimize cycle time and enhance the injection molding process efficiency.
Careful consideration of the material selection, part geometry, mold design, and insert positioning, you can achieve optimized molding operation and form top-quality, consolidated products.
Insert Molding Applications
Numerous industries currently employ plastic insert molding as the first-choice method of fabricating parts. Here are some of the sectors where application of insert molding process is prevalent:
Medical Devices
The injection molding process is valuable in fabrication of a myriad of medical devices from simple to complex and delicate types like implants and sutures. It also helps in production of components used in medical electronic devices.
Insert plastic molding use in medical industry entails fabrication of dental instruments, tubes and medical equipment. Moreover, it also helpful in production of medical knobs, surgical instruments, prosthetics, medical enclosures, and blades.
Aerospace
The aerospace sector utilizes insert injection molded parts in stowage bin latches, aircraft user interface switches, handles, and lavatories. They are also integral components in other aircraft parts like controls, communication, and interiors.
Telecommunication and Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronic and telecommunication devices extensively employ insert injection molding process in manufacturing of components like sensors, switches, and connectors. It facilitates integration of electrical components, circuitry, or metal contacts within the plastic casing, leading to a compact and effective product.
Automotive
This is another industry that has greatly adopted insert injection molding. Automotive manufacturers have successfully substituted metals components with more long-lasting plastic versions. Plastic insert molding helps in the manufacture of gears, electrical sensors, gears, and additional automotive components comprising of rubber/plastic and metal.
Defense
Defense industry uses insert-molded parts in control components, switches, and connectors. Embedding delicate metal contacts or circuitry inside a secure plastic encasing, insert injection molding ensures vibration resistance, enhanced reliability, and lowered weight.
Consumer Goods
Numerous consumer items, including personal care products, kitchen appliances, power tool housings, and toothbrush handles exploit insert injection molding. By enabling integration of plastic or metal inserts, the procedure offers enhanced ergonomics, strength and stability of the finished product.
Industrial Equipment
Another insert molding application is in fabrication of industrial machine components, including grips, housings, buttons, and knobs. These components improve the general performance, ergonomic design, and durability of the equipment.